17.09.2012
Project Management & Development Methodology - Part II
Project is a systematic, achieves the clients expected outcome and must complete with in the particular time period. Project management means by achieve what's in your mind.
Project Management.
- Four Disciplines of Project Management.
- Planning.
- Organizing.
- Managing.
- Controlling.
These four must have to achieve the project goals.
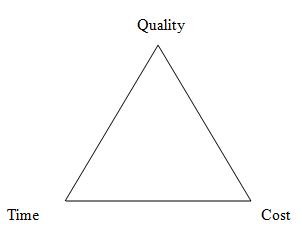
2. Aims to complete the project below three factors. Which are quality, time and cost.
Quality - How it servers to the clients requirements.
Time - How to complete it with in the given time period.
Cost - Cost should be not so much high, but it should be in a good quality.
If any of these factors changes it affect to the other two also.
3. Work to series of check points.
4. Control the project by utilizing software.
5. Project scheduled to the earliest possible date.
6. Delays identified to increase the resources.
ex: In Virtusa in this situations they uses employees who are in bench.
- These methodologies are uses to go through with the time logs and forward the work from that.
7. Use Information System development methodologies.
- Identify phases, techniques and deliverable s using the software development methodologies.
ex: Structured Systems Analysis and Design Methodology (SSADM).
- SSADM is a document driven methodology used by design, physical and logical.
- Doesn't have development phase.
- Used in requirements are uncertain. It means by it's difficult to understand the requirements.
8. Project should goes through a sequence of tasks / activities.
- It encounter with problems.
9. First break down project into tasks / activities.
- Use work break down structure to each employee.
ex: Gannt chart - It include with the time allocate to each task.
PERT chart (Program Evaluation Review Technique Chart).
- From these charts it identifies the each sub activity depends on the previous task that criticized on.
- Example of a PERT chart activity.
Activity Time (Weeks) Immediate Predecessors
A - Plan & schedule 5 -
B - Await hardware delivery 18 -
C - Programming 70 A
D - Install hardware 10 B
E - Program testing 30 C, D
F - Write user manual 25 D
G - Convert files 25 D
H - System test 25 E
I - User training 20 F
J - User test 25 G, H, I
Earliest Completion Time
(ECT), Latest Completion Time
(LCT), from those two Slack time and the Critical path will be calculate from the PERT chart.
Earliest Completion Time (ECT) = ETC of the preceding activity
+ duration
Latest Completion Time (LCT) = LCT of the prior activity –
duration
Total Slack Time = Latest Start -
Earliest Start
Critical path
- A series of events and activities with no slack time.
- At least one complete path will
exist where every node has equal ECTs and LCTs.
- If any task on the critical path
is delayed beyond its LCT, the entire project falls behind by that amount of time.
- In project management need to involves with slack activities as well.
10. Allocate time and resources to each task.
11. Inter relationships between activities established.
12. Using information critical path can be established.
Purpose of Project Manager.
- Make sure you do your work in proper time.
- Encourage the student.
- Provided advice.
- Make sure to bring log sheets and complete it.
Use of Log Sheet.
- Identify questions.
- Identify the things what you need to discuss.
- Notify what are the additional things need to ask from the project manager.
- Access performance to ask.
Preparation for Supervisor Meeting.
- Go through your work.
- Prepare for the list of questions.
- Be clear on your plan.
Learning gain of the Lecture.
Learn more information about the project management. Re prepare for the PERT chart. Gather information about the log sheet and how to preparation for the supervisor meeting.
Personal Opinion.
This is another important lecture for the final year project.

No comments:
Post a Comment